Amorphous Material Is Best Described as
A dislocation in an. Some examples of amorphous solids they are thermoplastic polymers thermoset polymers elastomers expandable polymers or glass.

Amorphous Solid Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Being without definite character or nature.

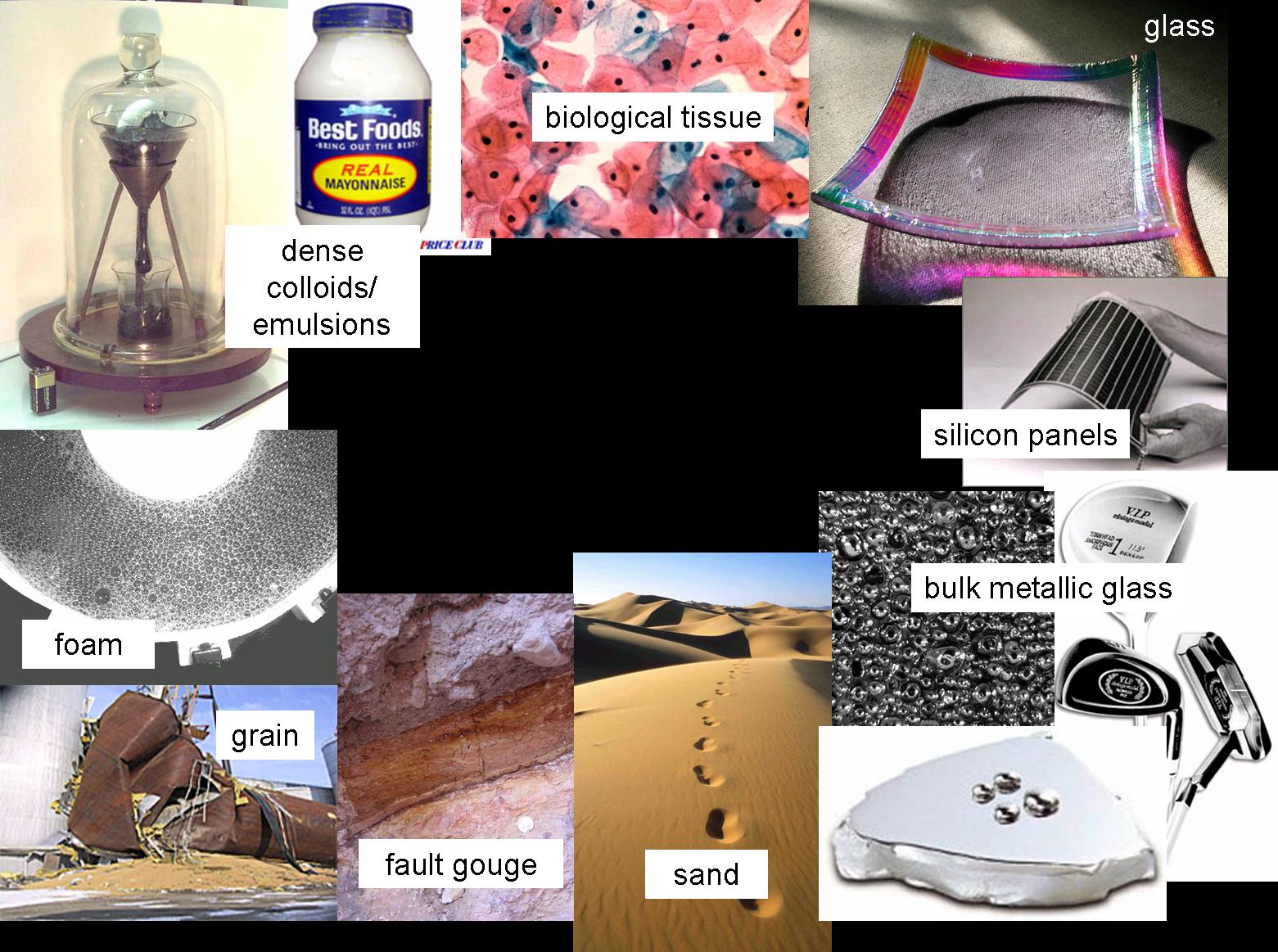
. It was once thought that relatively few materials could be prepared as amorphous solids and such materials notably oxide glasses and organic polymers were called glass-forming solids. We distinguish at least four categories of amorphous glassy materials. A glass is a solid that has been cooled too quickly to form ordered crystals.
Amorphous materials are those that have no detectable crystal structure. Such materials can be found in nature and also have a. Just like in liquids in amorphous solids properties such as electrical conductivity thermal conductivity mechanical strength refractive index etc remain the same in all directions.
Amorphous materials cannot contain dislocations. Amorphous material is one In which there is no definite atomic structure and atoms exist in a random pattern just as in a liquid. Amorphous film materials can be formed by.
Amorphous solids display several of the characteristics of a liquid. Unclassifiable an amorphous segment of society. Rapid quench 105 Ks X-ray amorphous forms include any material structural coherence length is or the order of 5 basic units eg.
Semi-crystalline polymers have a partly different structure. 10 Examples of Amorphous Solids. The term glassy has the same structural.
More recent additions to the family of amorphous solids are synthetic polymers 1940s and metallic glasses 1960s. The best way to differentiate between amorphous and crystalline materials is to measure XRD patterns. The dislocation density in an amorphous material is normally less than the dislocation density in a crystalline material with the same composition.
Iii organic and inorganic thermoplastics. The intermolecular forces are not equal. Preparation of amorphous solids.
Amorphous materials cannot contain dislocations. Crystalline material always exhibit sharp diffraction peaks. Deviations in the C-C distances greater than 5 occur in such materials as well as deviations in the bond.
Rigid pre-f abricated components and adhesi vecompliant pre-f abricated parts and amorphous ma-terials that cure into solids. Amorphous alloys are a class of metal. Almost any substance can solidify in amorphous form if the liquid phase is cooled rapidly enough.
An amorphous translucent solid is called a glass An amorphous translucent solid. It has irregular arrangement of solid particles. They are also called supercooled liquidsThey are isotropic.
Also the distance between particles varies. A portion of their polymer chains 20-80 depending on the material have arranged to tight and strictly orientated crystals. This paper focuses on the models of atomic arrangements in amorphous materials.
Amorphous comes from the Greek where the prefixais negation and the word morfo means form that is formless. An amorphous material AM has a non-crystalline structure that differs from that of its iso-chemical liquid and does. Man made inorganic glasses date back to ancient civilisations Summeria Egypt.
Hence they are known as isotropic materials. The remaining chains are in an amorphous state surrounding the crystals. Shapeless an amorphous cloud mass.
The table of representative amorphous solids. II as are the three material choices. In the absence of cleavage and other direct proofs of crystal- linity we must rely largely upon optical tests for transparent and translucent minerals.
Deposition at low temperatures where the adatoms do not have enough mobility to form a crystalline structure quenching. Atoms molecules unit cells. Section III describes mechanisms.
Which of the following is the an amorphous material. The requirements for amorphous materials to be suitable for robotic construction are described in Sec. Modern approach is to carry out computer simulations with prediction that can be tested by experiments.
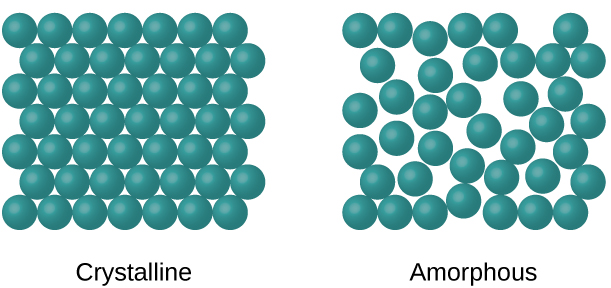
Materials that have a disordered structure with no regular repeating pattern are described as amorphous. The terms amorphous and non-crystalline are synonymous under this definition. The terms amorphous and non-crystalline are synonymous under this definition.
And iv amorphous permanent networks. Amorphous ice is most likely the most common form of water in space. There are naturally occurring amorphous materials such as obsidian mineral vitrified rocks and solidified organic materials such as amber.
Amorphous plastic can only be used in temperatures below their Tg. Having no definite form. They have undefined geometric shape.
It is now known that the amorphous solid state is almost a universal property of condensable matter. Amorphous materials are condensed phases which do not possess the long-range translational or orientational order or periodicity characteristic of a crystal. Which of the following statements best describes the nature of dislocations in an amorphous material.
This word is derived from Greek. The term amorphous carbon is restricted to the description of carbon materials with localised π-electrons as described by PWAnderson. Pyrolusite for example is probably an amorphous manganese dioxid produced by the dehydration of crystalline manganite which accounts for its fibrous structure.
The earliest ideas of Bernal on the structure of liquids were followed by experiments and computer models for the packing of spheres. The Tg of an amorphous material is defined as the transition temperature between the glassy state solid-like material and the rubbery state liquid-like material. The dislocation density in an amorphous material is normally less than the dislocation density in a crystalline material with the same composition.
The dislocation density in an amorphous material is normally greater than the dislocation density in a crystalline material with the same composition. When we speak of amorphous solids we speak of a solid state of matter. Liquids Glasses crushed Crystals sometimes Meso-phases sometimes and potentially very small.
Comprehensive Biotechnology Second Edition 2011. The term glassy has the same structural meaning but in addition it also usually implies that the material exhibits a glass transition. Deposition of a natural glassy material such as a glass composition.

Crystalline And Amorphous Solids Explanation Differences Examples Etc

Comments
Post a Comment